RADIO-FREQUENCY IDENTIFICATION TAGS
(Also known as RFID tags)
LETS START THIS WIKI OFF WITH A LITTLE QUIZ!
YES THAT'S RIGHT. IN THIS AMAZING WIKI PAGE, YOU WILL LEARN MORE THAN YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT RADIO-FREQUENCY IDENTIFICATION TAGS! FUN EH?
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. What is it?
2. History
3. The physics behind it all
4. Types of RFID
5. Application
6. Price
7. Standardization
8. Cool stuff
9. Thinking question
10. Sources
1. WHAT IS IT??
After watching our amazingly interesting slideshow, you probably already know what an RFID tag is. Congrats to you if you do. If you don't, then just keep reading...
Radio-frequency identification tag, also known as RFID tag, is a technology which serves the purpose of identification and tracking by using radio waves to exchange data between a reader and an electronic tag attached to an object.
Yes, RFID scanners and tags are most commonly found at the entrances of retail stores to detect customer theft right away. If you have ever tried to take something from a store without paying, you probably already know about this amazing technology. RFID scanners also can provide each product in a grocery store with its own unique identifying number. ALSO, these tags can provide assets/people/medical devices/etc, all with individual unique identifiers! Sort of like a name tag for every single thing. This is a huge improvement over paper and pencil tracking or bar code tracking that has been used since the 1970's.
Just in case you forgot all that, we've hired an expert in the field to refresh your memory.
Don't you want to know who made this amazing technology? Of course you do. :)
2. HISTORY
The history of RFID technology can be traced back as far as World War II. The Germans, Japanese, British and Americans were using radar to detect approaching planes from far away. The British in particular developed a system in which they put a transmitter on each British plane, to distinguish them from the enemy planes. When the radar stations received their signals, it broadcasted a signal back that identified the aircraft as friendly, which is the basic concept of RFID. In the 1950s and 1960s, it was discovered that radio frequency energy can be used to identify objects remotely, specifically if items were stolen or paid for. Soon companies began commercializing anti-theft systems for use in the general public.
Japanese, British and Americans were using radar to detect approaching planes from far away. The British in particular developed a system in which they put a transmitter on each British plane, to distinguish them from the enemy planes. When the radar stations received their signals, it broadcasted a signal back that identified the aircraft as friendly, which is the basic concept of RFID. In the 1950s and 1960s, it was discovered that radio frequency energy can be used to identify objects remotely, specifically if items were stolen or paid for. Soon companies began commercializing anti-theft systems for use in the general public.
RFID Patents
The first US patent was given to Mario W. Cardullo for an active RFID tag with rewritable memory on January 23, 1973.

Charles Walton, a California entrepreneur, received a patent later that same year for a passive transponder that was used to unlock a door without a key. The device was a card with an embedded transponder that sent a signal to a reader near the door. If the reader detects a valid identity number stored within the tag, the reader unlocks the door.
In the 1970s, a system was developed in which a transponder was installed in a truck and readers at the gates of secure facilities. The transponder in the truck would send their ID and other data to the reader. This was commercialized in the mid-1980s in the form of automated toll payment systems. They are now widely used on road, bridges and tunnels.
Now you have a better understanding of who was behind this revolutionary idea, let's look at the physics behind it all! Don't fall asleep yet!

3. THE PHYSICS BEHIND RFID TECHNOLOGY
The RFID technology uses radio waves to transmit data between its readers and its tags.
What is a wave?
A wave is a disturbance which carries energy from one place to another. And radio waves are created when electrons are passed through a conductor. The current also creates a magnetic field. The fluctuations in the current produces changes in the magnetic field, crating waves of electromagnetic energy. These are called electromagnetic waves.
Electromagnetic waves? What? Don’t panic!! There are many types of electromagnetic waves you encounter in your daily lives: radio waves, microwaves, x-rays, and light. RFID reader and tags use radio waves to communicate!
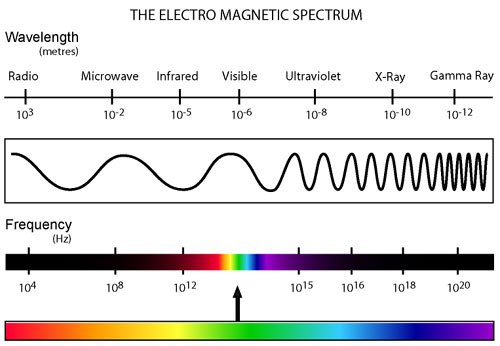
Now you might be thinking: there are soooo many cool types of waves, so why radio waves???
Well, radio waves are low-frequency waves which means they oscillate slowly, and their wavelengths are longer. Radio waves are also capable of passing through materials such as plastic, cardboard, wood, cloth, etc.
Plastic:

Cardboard:

Wood:

Cloth:

The radio waves RFID systems transmit between the reader and the tag carries information and data which can be decoded and extracted when the receiver receives the wave. This is how companies, hospitals, financial institutions, libraries, and many more places use RFID readers and tags to keep track of inventory or prevent theft. Butttttttt, more will be on that later in the APPLICATION section of our wiki. So…STAY TUNED!!!!
The process of emitting and receiving signals:
1. The reader continuously emits RF carrier signals, and keeps observing the received RF signals for data.
2. A tag modulates the radio frequency field, and the same is detected by the reader.
3. The tag absorbs a small portion of the energy emitted by the reader, and starts sending modulated information when sufficient energy is acquired from the radio frequency field generated by the reader.
4. The reader demodulates the signals received from the tag antenna, and decodes the same for further processing.

DOESN'T THE PHYSICS BEHIND RFID READERS AND TAGS RELATE SOOO MUCH TO OUR FIELDS UNIT? I THINK SO.
4. TYPES OF RFID
In general, there are only two types of RFID tags.
Fixed RFID: If the reader reds the tags in a stationary position, it is called a fixed RFID. These fixed readers are set up specific interrogation zones that can be tightly controlled if the physics is well engineered. This allows a very definitive reading area for when tags go in and out of the interrogation zone.
Mobile RFID: if the reader is mobile when the reader reads tags, it is called mobile RFID. Mobile readers include hand helds, carts and vehicle mounted RFID readers from manufacturers such as Motorola, Intermec, Impinj, Sirit, etc.
ALSOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOO!
RFID can be either:
Passive- using no battery
Active- on board battery that always broadcasts its signals.
Battery assisted passive- a small battery on board that is activated when in the presence of an RFID reader.
5. APPLICATIONS
DO RFID TAGS AFFECT YOUR LIFE? OH YESSSS. RFID tags can be sensed or detected wirelessly through the use of radio frequency technology. RFID tags are used in many applications such as library books, healthcare, security access systems and other stuff. RFID system usually consists of a transponder which has a microchip and an antenna.
1. RFID tags in library
Each RFID tag has a special identification number and it can have additional information like a location of a book or short description about the book. If one tries to steal a library book, the RFID scanners at the door would beep. AND YOU WOULD GET CAUGHT!

2. Ticketing
RFID card transponders can be attached to every consumer and it can be only available for specific time and periods. Tickets are read remotely to increase the throughput at the entrance. Eg. A ski ticket allows the tourist to go in without having to do anything.

3. Enterprise Usage
Enterprise supply chain management to improve the efficiency of inventory tracking and management.
Many financial institutions use RFID to track key assets and automate Sarbanes Oxley SOX compliance.
 Here's ANOTHER application:
Here's ANOTHER application:

Now do you see how much RFID technology helps YOUR life??
6. PRICE
Passive tags:
start at $ .05 each and for special tags meant to be mounted on metal, or withstand gamma sterilization go up to $5.
Active tags:
which can be used to identify medical assets, or to monitor external envionmental conditions.in data centers all start at $50 and can go up over $100 each!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
BAP tags:
in the $3–10 range and also have sensor capability like temperature and humidity.
7. STANDARDIZATION
There are a variety of groups defining standards and regulating the use of RFID, including:
- the International Organization for Standardization(ISO)
- the International Electrotechnical Commission(IEC)
- ASTM International
- the DASH7Alliance and EPCglobal
- the Financial Services Technology Consortium(FSTC)
8. COOL STUFF
To amuse you, here is a CARTOON about RFID? I know right, there's actually a cartoon about this topic....

http://autoid.mit.edu/pickup/RFID_Papers/008.pdf
9. THINKING QUESTION
Think about this carefully, then discuss among your peers.
RFID Tags THINKING QUESTION.docx
10. SOURCES CITED
http://www.rfidjournal.com/article/view/1338/2
http://www.rfidjournal.net/live05/sunday/RFIDU_1230pm_thorne.pdf
http://www.slais.ubc.ca/courses/libr500/04-05-wt2/www/T_Gnissios/libraries.htm
http://www.priv.gc.ca/fs-fi/02_05_d_28_e.cfm
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Radio-frequency_identification
http://electronics.howstuffworks.com/gadgets/high-tech-gadgets/rfid.htm
http://www.mmt-inst.com/RFID%20applications%20in%20manufacturing%20_Draft%207_.pdf
http://www.rfid-handbook.de/rfid/physics.html
RECENT VISITORS:
You now
Someone else 5 hrs ago
Someone else 15 hrs ago
MUSIC:
13-nature Soft Music 1 03-i'll Have To Say I Love You In A Song